libquadflash API¶
The libquadflash library provides functions for reading and writing data to Quad-SPI flash devices that use the xCORE format shown in the diagram below.
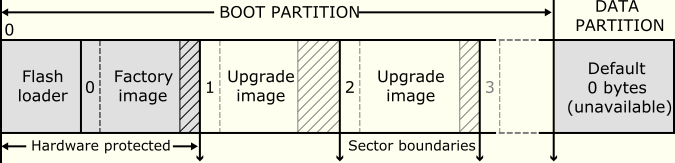
Flash format diagram¶
All functions are prototyped in the header file
<quadflash.h>. Except where otherwise stated, functions
return 0 on success and non-zero on failure.
General Operations¶
The program must explicitly open a connection to the Quad-SPI device before attempting to use it, and must disconnect once finished accessing the device.
The functions fl_connect and fl_connectToDevice require an
argument of type fl_QSPIPorts, which defines the four ports and
clock block used to connect to the device.
typedef struct {
out port qspiCS;
out port qspiSCLK;
out buffered port:32 qspiSIO;
clock qspiClkblk;
} fl_QSPIPorts;
-
int fl_connect(fl_QSPIPorts *SPI)¶
fl_connectopens a connection to the specified Quad-SPI device.
-
int fl_connectToDevice(fl_QSPIPorts *SPI, fl_DeviceSpec spec[], unsigned n)¶
fl_connectToDeviceopens a connection to an Quad-SPI device. It iterates through an array of n Quad-SPI device specifications, attempting to connect using each specification until one succeeds.
-
int fl_getFlashType(void)¶
fl_getFlashTypereturns anenumvalue for the flash device. The enumeration of devices known to libquadflash is given below.typedef enum { UNKNOWN = 0, ISSI_IS25LQ016B, ISSI_IS25LQ032B, ISSI_IS25LQ080B, SPANSION_S25FL116K, SPANSION_S25FL132K, SPANSION_S25FL164K, } fl_QuadFlashId;
If the function call
fl_connectToDevice(p, spec, n)is used to connect to a flash device,fl_getFlashTypereturns the parameter valuespec[i].flashIdwhereiis the index of the connected device.
-
unsigned fl_getFlashSize(void)¶
fl_getFlashSizereturns the capacity of the Quad-SPI device in bytes.
-
int fl_disconnect(void)¶
fl_disconnectcloses the connection to the Quad-SPI device.
Boot Partition Functions¶
By default, the size of the boot partition is set to the size of the flash device. Access to boot images is provided through an iterator interface.
-
int fl_getFactoryImage(fl_BootImageInfo *bootImageInfo)¶
fl_getFactoryImageprovides information about the factory boot image.
-
int fl_getNextBootImage(fl_BootImageInfo *bootImageInfo)¶
fl_getNextBootImageprovides information about the next upgrade image. Once located, an image can be upgraded. Functions are also provided for reading the contents of an upgrade image.
-
unsigned fl_getImageVersion(fl_BootImageInfo *bootImageInfo)¶
fl_getImageVersionreturns the version number of the specified image.
-
int fl_startImageReplace(fl_BootImageInfo*, unsigned maxsize)¶
fl_startImageReplaceprepares the Quad-SPI device for replacing an image. The old image can no longer be assumed to exist after this call.Attempting to write into the data partition or the space of another upgrade image is invalid. A non-zero return value signifies that the preparation is not yet complete and that the function should be called again. This behavior allows the latency of a sector erase to be masked by the program.
-
int fl_startImageAdd(fl_BootImageInfo*, unsigned maxsize, unsigned padding)¶
fl_startImageAddprepares the Quad-SPI device for adding an image after the specified image. The start of the new image is at least padding bytes after the previous image.Attempting to write into the data partition or the space of another upgrade image is invalid. A non-zero return value signifies that the preparation is not yet complete and that the function must be called again. This behavior allows the latency of a sector erase to be masked by the program.
-
int fl_startImageAddAt(unsigned offset, unsigned maxsize)¶
fl_startImageAddAtprepares the Quad-SPI device for adding an image at the specified address offset from the base of the first sector after the factory image.Attempting to write into the data partition or the space of another upgrade image is invalid. A non-zero return value signifies that the preparation is not yet complete and that the function must be called again.
-
int fl_writeImagePage(const unsigned char page[])¶
fl_writeImagePagewaits until the Quad-SPI device is able to accept a request and then outputs the next page of data to the device. Attempting to write past the maximum size passed tofl_startImageReplace,fl_startImageAddorfl_startImageAddAtis invalid.
-
int fl_writeImageEnd(void)¶
fl_writeImageEndwaits until the Quad-SPI device has written the last page of data to its memory.
-
int fl_startImageRead(fl_BootImageInfo *b)¶
fl_startImageReadprepares the Quad-SPI device for reading the contents of the specified upgrade image.
-
int fl_readImagePage(unsigned char page[])¶
fl_readImagePageinputs the next page of data from the Quad-SPI device and writes it to the array page.
-
int fl_deleteImage(fl_BootImageInfo *b)¶
fl_deleteImageerases the upgrade image with the specified image.
Data Partition Functions¶
All flash devices are assumed to have uniform page sizes but are not assumed to have uniform sector sizes. Read and write operations occur at the page level, and erase operations occur at the sector level. This means that to write part of a sector, a buffer size of at least one sector is required to preserve other data.
In the following functions, writes to the data partition and erasures from the data partition are not fail-safe. If the operation is interrupted, for example due to a power failure, the data in the page or sector is undefined.
-
unsigned fl_getDataPartitionSize(void)¶
fl_getDataPartitionSizereturns the size of the data partition in bytes.
-
int fl_readData(unsigned offset, unsigned size, unsigned char dst[])¶
fl_readDatareads a number of bytes from an offset into the data partition and writes them to the array dst.
-
unsigned fl_getWriteScratchSize(unsigned offset, unsigned size)¶
fl_getWriteScratchSizereturns the buffer size needed byfl_writeDatafor the given parameters.
-
int fl_writeData(unsigned offset, unsigned size, const unsigned char src[], unsigned char buffer[])¶
fl_writeDatawrites the arraysrcto the specified offset in the data partition. It uses the arraybufferto preserve page data that must be re-written.
Page-Level Functions¶
-
unsigned fl_getPageSize(void)¶
fl_getPageSizereturns the page size in bytes.
-
unsigned fl_getNumDataPages(void)¶
fl_getNumDataPagesreturns the number of pages in the data partition.
-
unsigned fl_writeDataPage(unsigned n, const unsigned char data[])¶
fl_writeDataPagewrites the array data to the n-th page in the data partition. The data array must be at least as big as the page size; if larger, the highest elements are ignored.
-
unsigned fl_readDataPage(unsigned n, unsigned char data[])¶
fl_readDataPagereads the n-th page in the data partition and writes it to the array data. The size of data must be at least as large as the page size.
Sector-Level Functions¶
-
unsigned fl_getNumDataSectors(void)¶
fl_getNumDataSectorsreturns the number of sectors in the data partition.
-
unsigned fl_getDataSectorSize(unsigned n)¶
fl_getDataSectorSizereturns the size of the n-th sector in the data partition in bytes.
-
unsigned fl_eraseDataSector(unsigned n)¶
fl_eraseDataSectorerases the n-th sector in the data partition.
-
unsigned fl_eraseAllDataSectors(void)¶
fl_eraseAllDataSectorserases all sectors in the data partition.